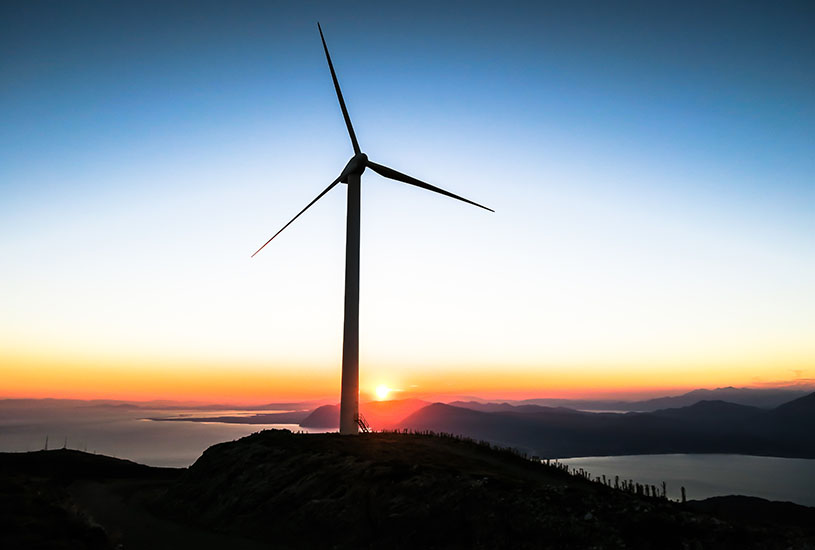
Carbon fibre composites are set to improve the performance of wind turbines and benefit the local and global renewable energy sector.
Deakin University is partnering with leading wind energy solution provider Vestas, to improve the compressive strength of carbon fibre composite materials for wind turbines.
Deakin Carbon Nexus Director Derek Buckmaster said that along with the potential to improve wind turbine performance, the partnership underscored possible expansion of Geelong’s composite research and manufacturing footprint and would help Victoria achieve its Renewable Energy Target (VRET).
“We are delighted to work with Vestas to achieve these goals,” Mr Buckmaster said. “The combination of Deakin’s research expertise from the world-leading composites research team at Carbon Nexus, and Vestas’ industry capabilities has the potential to take composite materials research to the next level, delivering real-world outcomes for Victoria.”
Carbon fibre composites are a critical material to the further improvement of wind turbine blades, due to their unmatched strength-to-weight ratio, enabling the manufacture of longer blades which improve efficiency and lower cost.
[testimonial_text]Power generated is proportional to wind speed and so higher wind speed has a dramatic effect of increased electricity. Longer blades sweep out a larger wind area and are, by necessity, installed on larger towers. This places them in a better position to capture greater wind speeds further from the ground.[/testimonial_text]
[testimonial_picture name=”Mr Derek Buckmaster” details=”Deakin Carbon Nexus Director”]
 [/testimonial_picture]
[/testimonial_picture]The uptake of carbon fibre composites has been one of the main drivers behind the increased turbine efficiency and competitiveness of wind power in recent years. Turbine blades are now the largest single use for carbon fibre, accounting for over 40 per cent of global production.
Dr Adrian Gill, global lead specialist for blade structure and material at Vestas, noted the importance of investing in further materials research.
“With carbon fibre composite innovations, we can increase the performance of turbine blades. Stronger carbon fibre will allow us to reduce the required amount of carbon fibre used in the blade, so the blade will be lighter and cheaper. This makes renewable energy cleaner and more affordable and supports the development of Australia’s growing wind energy sector,” Dr Gill said.
Vestas Asia Pacific President Clive Turton highlighted the importance of the Victorian Government’s renewable energy targets and auction strategy to the local renewable energy industry.
“Improved composite material will bring revolutionary benefit to renewable industry locally and globally. By improving efficiency and driving down the cost of wind turbines, we are providing Victoria, Australia and the world with clean and more affordable energy,” Mr Turton said.
“Breakthroughs in composite materials will benefit the wind industry and may deliver significant commercial outcomes in other industries.”
“Our new partnership leverages Deakin’s leadership in carbon fibre composites and Vestas’ expertise as a leading global player in the wind energy sector. It is a powerful combination that will position Geelong and Victoria at the forefront of wind energy innovation and commercialisation.”
The $34m Carbon Nexus research facility has already attracted many local innovative carbon fibre parts manufacturers, such as Carbon Revolution and Quickstep, and global carbon fibre manufacturer LeMond.
With strong State Government support, Geelong is fast becoming a globally relevant centre of excellence for composite research and advanced carbon fibre-based manufacturing. The research with Vestas is conditional on awards to Vestas Supported Projects under the Victorian Renewable Energy Auction Scheme.
Published by Deakin Research on 18 June 2018