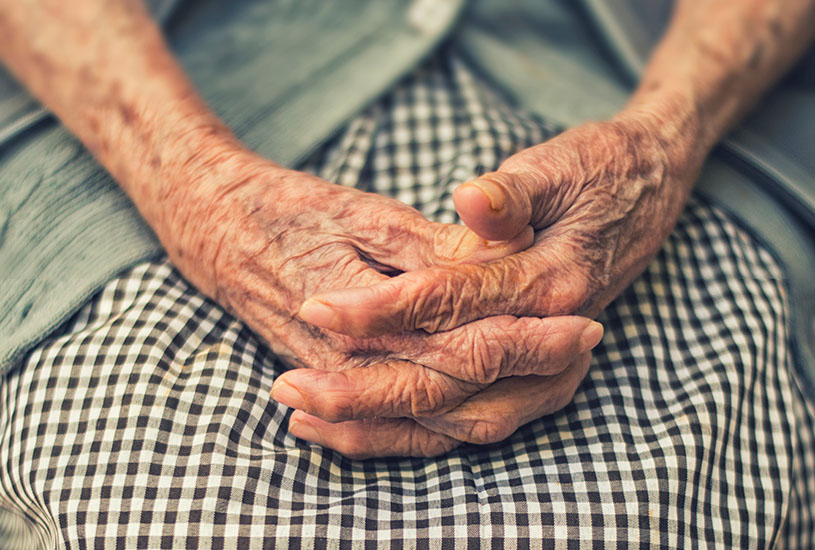
New Deakin research highlights the growing number of adult children caring for their ageing parents, and the health issues it can exacerbate for older people and caregivers alike.
Caring for Australia’s growing ageing population is major issue for the country – and families.
“The care provided to older parents in the community by adult children is significant, currently saving the Federal Government over $4.4 billion annually,” said Associate Professor Gery Karantzas, from Deakin University’s School of Psychology.
“By 2025, families will be expected to provide much of the primary care for ageing parents as the Government and aged care providers struggle to meet the welfare needs of our rapidly ageing society.”
However, Associate Professor Karantzas said caring for ageing parents came at a cost for their families, with many adult children report significant carer stress and burnout due to the financial, social and emotional strains that caregiving can place on carers.
Associate Professor Karantzas is lead researcher on the School of Psychology’s Families in Later Life Study, which is tracking adult children caring for ageing parents in the community over a one-year period.
The study is focusing on the quality of the relationship between the parent and child, which can have a big impact on health outcomes for both parties.
According to Associate Professor Karantzas, the quality of family relationships during the later years of life can exacerbate the strains caused by caring for an elderly parent.
He said preliminary findings from the study showed families suffering relationship strains demonstrated poorer care of older parents.
“This is especially the case when the carer is more distressed,” he said. “The idea that families pull together to help out mum and dad may not represent the reality of ageing families. For some, the stress and strains of caring for an older parent merely widen the cracks that already exist.
“Family relationships marked by rejection or a sense that one is not good enough can exacerbate negative outcomes including problems with immune functioning and increased risk of depression, anxiety and stress.
[testimonial_text]There’s even preliminary evidence to suggest that relationship strains can exacerbate rates of cognitive decline in both carers and care-recipients.[/testimonial_text]
[testimonial_picture name=”Associate Professor Gery Karantzas” details=”Deakin University School of Psychology”]
 [/testimonial_picture]
[/testimonial_picture]In contrast, family relationships reflecting love and support appeared to decrease these physical and mental health issues, Associate Professor Karantzas said.
“It’s as if good family relationships inoculate ageing parents and their sons and daughters from all kinds of physical and emotional problems.”
How best to support these positive outcomes is what Associate Professor Karantzas hopes to better understand through the Families in Later Life Study.
“This study is unique in that it tracks the relationship and wellbeing of both the older parent and their sons and daughters, thereby investigating both perspectives,” he said.
“Most aged care studies track either the carer or the care-recipient, but not both. And yet, it’s the interaction between the adult child and older parent that is critical in understanding how care is provided, how it’s received, and how parents and children influence one another’s wellbeing.”
Associate Professor Karantzas said the study’s findings would provide crucial ways to support and strengthen family bonds.
“It will also assist the future development of services for family caregivers and care recipients to cope with this already difficult stage of life,” he added.
Associate Professor Karantzas and his team are currently looking for families from the Melbourne and Geelong regions to take part in the Families in Later Life Study. To find out more, visit www.fills.org.au or phone (03) 9246 8544.
Published by Deakin Research on 24 January 2018